_pddqnqv8.png)
Bio Reagents & Consumables
- Home
- Products
- Bio Reagents & Consumables
- Immunoassay
- ELISA (Enzyme-linked Immunosorbent Assay)
- ELK1156 Human IL6 (Interleukin 6) ELISA Kit
ELISA (Enzyme-linked Immunosorbent Assay)
ELK1156 Human IL6 (Interleukin 6) ELISA Kit
Overview
| Product name: | Human IL6(Interleukin 6) ELISA Kit |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Alternative Names: | IL-6;MGI2-A; MGI2A; HGF; BSF2; HSF; IFNB2; B-Cell Stimulatory Factor-2; Hybridoma/Plasmacytoma Growth Factor; Hepatocyte Stimulating Factor; Cytotoxic T-Cell Differentiation Factor |
| Assay Type: | Sandwich |
| Sensitivity: | 3.2 pg/mL |
| Standard: | 500 pg/mL |
| Detection Range: | 7.82-500 pg/mL |
| Sample Type: | serum, plasma, tissue homogenates, cell lysates, cell culture supernates and other biological fluids |
| Assay Length: | 3.5h |
| Research Area: | Cytokine;Tumor immunity;Infection immunity;Cardiovascular biology; |
| Test principle: | The test principle applied in this kit is Sandwich enzyme immunoassay. The microtiter plate provided in this kit has been pre-coated with an antibody specific to Human IL6. Standards or samples are added to the appropriate microtiter plate wells then with a biotin-conjugated antibody specific to Human IL6. Next, Avidin conjugated to Horseradish Peroxidase (HRP) is added to each microplate well and incubated. After TMB substrate solution is added, only those wells that contain Human IL6, biotin-conjugated antibody and enzyme-conjugated Avidin will exhibit a change in color. The enzyme-substrate reaction is terminated by the addition of sulphuric acid solution and the color change is measured spectrophotometrically at a wavelength of 450nm ± 10nm. The concentration of Human IL6 in the samples is then determined by comparing the OD of the samples to the standard curve. |
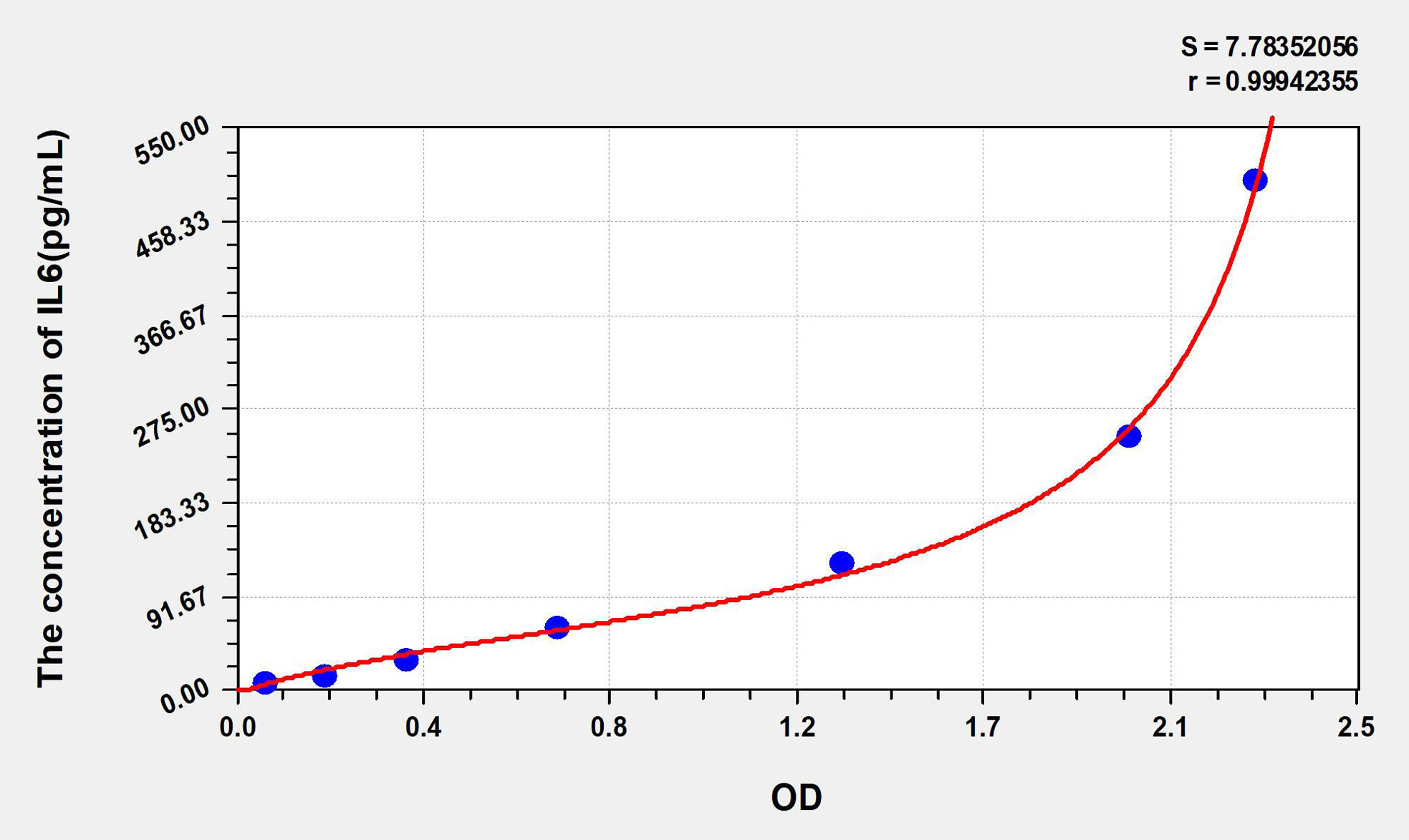
Standard curve
| Concentration (ng/mL) | OD | Corrected OD |
|---|---|---|
| 500.00 | 2.328 | 2.260 |
| 250.00 | 2.045 | 1.977 |
| 125.00 | 1.412 | 1.344 |
| 62.50 | 0.780 | 0.712 |
| 31.25 | 0.444 | 0.376 |
| 15.63 | 0.262 | 0.194 |
| 7.82 | 0.132 | 0.064 |
| 0.00 | 0.068 | 0.000 |
Precision
Intra-assay Precision (Precision within an assay): CV%<8%
Three samples of known concentration were tested twenty times on one plate to assess intra-assay precision.
Inter-assay Precision (Precision between assays): CV%<10%
Three samples of known concentration were tested in forty separate assays to assess inter-assay precision.
Recovery
Matrices listed below were spiked with certain level of recombinant IL6 and the recovery rates were calculated by comparing the measured value to the expected amount of IL6 in samples.
| Matrix | Recovery range | Average |
|---|---|---|
| serum(n=5) | 97-105% | 101% |
| EDTA plasma(n=5) | 87-99% | 92% |
| Heparin plasma(n=5) | 88-107% | 94% |
Linearity
The linearity of the kit was assayed by testing samples spiked with appropriate concentration of IL6 and their serial dilutions. The results were demonstrated by the percentage of calculated concentration to the expected.
| Matrix | 1:2 | 1:4 | 1:8 | 1:16 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| serum(n=5) | 86-93% | 91-103% | 87-98% | 92-99% |
| EDTA plasma(n=5) | 89-99% | 83-96% | 98-104% | 88-101% |
| Heparin plasma(n=5) | 85-102% | 84-99% | 97-101% | 89-102% |
| Details | Kindly refer to the "Overview" tab. |
Author: Yang Yang, Jiajun Chen, Jiashen Yang, Chengla Yi, Fan Yang, Wei Gao, Zhanfei Li, Xiangjun Bai
Publication: Clinica Chimica Acta
IF: 2.695
Despite significant advances in the diagnosis and management of sepsis and trauma over the past few decades, severe infection and injury continue to represent major public health challenges. Fibrinogen-like protein 2 (FGL2), a member of the fibrinogen family, can be expressed as a membrane-associated protein with coagulation activity or in a secreted form possessing unique immune suppressive functions. In this study, we evaluated whether soluble fibrinogen-like protein 2 (sFGL2) can serve as a biomarker to predict the development of sepsis in trauma patients.
Author: Zhen-tao Mo, Yu-ling Liao, Jie Zheng, Wen-na Li
Publication: Life Sciences
IF: 5.037
Icariin (ICA), a flavonol glycoside isolated from Epimedium, has been considered as a potential alternative therapy for ischemic stroke. However, the protective mechanisms of ICA on cerebral ischemia-reperfusion (I/R) are not fully illuminated yet. The effects of ICA on ER stress and inflammatory response which were involved in the pathological process of cerebral I/R were investigated in vitro. Microglia and neurons were subjected to OGD/R. ICA was administrated to microglia 1 h before OGD and maintained 2 h throughout OGD. At 24 h after reoxygenation, the protein expression of IL-1 β, IL-6, TNF-α in the supernatant of microglia was measured using ELISA assay; neuronal apoptosis was assessed by TUNEL staining; and cell viability was detected using CKK-8 assay; the expression of IRE1α, XBP1u, XBP1s, and cleaved caspase-3 in neurons was examined by western blotting and qRT-PCR; the expression of p-IRE1α in neurons was detected by western blotting. We found that OGD/R induced the expression of IL-1 β, IL-6, TNF-α in the supernatant of microglia; OGD/R and these proinflammatory cytokines promoted the mRNA as well as protein expression of XBP1u, XBP1s and cleaved caspase-3, increased the ratio of p-IRE1α/IRE1α, as well as apoptosis, and decreased cell viability in primary cortical neurons, while ICA reversed the levels of the above factors. IRE1 overexpression enhanced ER stress as well as apoptosis, and impaired the protective effects of ICA. These results suggested that ICA can inhibit apoptosis in neurons after OGD/R through IRE1/XBP1 signaling pathway beside its anti-inflammatory effect.
Author: Huqun Li, Chongshu Wang, Jiefang Zhao, Cuilian Guo
Publication: Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy
IF: 6.529
c-jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) plays pivotal roles in many physiological processes, including inflammation and glucose metabolism. However, the effects of JNK on olanzapine-induced insulin resistance and the underlying mechanisms have not been fully elucidated. The aim of our study was to explore the role of JNK in olanzapine-induced insulin resistance and the underlying mechanisms.
Author: Meng Wang, Jielin Deng, Huanzhu Lai, Yanqiu Lai, Guannan Meng, Zhenya Wang, Zhen Zhou, Hu Chen, Zhiyao Yu, Shuyan Li and Hong Jiang
Publication: Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity
IF: 6.543
Objective. In renal ischemia/reperfusion injury (RIRI), nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) initiates the expression of multiple genes involved in inflammatory disease. Inhibition of NF-κB-mediated inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) expression can ameliorate RIRI. Vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) protects against various organs I/R injury. The present study was designed to elucidate the protective effect of VNS on RIRI and its influence on iNOS protein expression. Methods. Eighteen male Sprague-Dawley rats were randomly allocated into the sham group, the I/R group, and the VNS+I/R group, 6 rats per group. An RIRI model was induced by a right nephrectomy and blockade of the left renal pedicle vessels for 45 min. After 6 h of reperfusion, the blood samples and renal samples were collected. The VNS treatment was performed throughout the I/R process in the VNS+I/R group using specific parameters (20 Hz, 0.1 ms in duration, square waves) known to produce a small but reliable bradycardia. Blood was used for evaluation of renal function and inflammatory state. Renal injury was evaluated via TUNEL staining. Renal samples were harvested to evaluate renal oxidative stress, NF-κB p65 levels, and iNOS protein expression. Results. The VNS treatment reduces serum creatinine (Cr) and blood urea nitrogen (BUN) levels. Simultaneously, the levels of tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α), interleukin 6 (IL-6), and interleukin 1-beta (IL-1β) were significantly increased in the I/R group, but VNS treatment markedly ameliorated this inflammatory response. Furthermore, the VNS ameliorated oxidant stress and renal injury, indicated by a decrease in 3-nitrotyrosine (3-NT) formation and MDA and MPO levels and an increase in the SOD level compared to that in the I/R group. Finally, the VNS also significantly decreases NF-κB p65, iNOS, and nitrite/nitrate levels compared to that in the I/R group. Conclusion. Our findings indicate that NF-κB activation increased iNOS expression and promoted RIRI and that VNS treatment attenuated RIRI by inhibiting iNOS expression, oxidative stress, and inflammation via NF-κB inactivation.
Author: Syed Anees Ahmed, Irshad Reza, Athar Husain, Pragati Singh, Jiaur R Gayen
Publication: Phytomedicine Plus
IF: -
Background Cissus quadrangularis L. is commonly known as hadjod and traditionally used as a medicinal plant for the treatment of osteoporosis, dyspepsia, tumors, chronic ulcers, and hepatic diseases. Existing studies have proclaimed the proinflammatory property of NOX4 through instigating ROS and oxidative stress, which is considered to be one of the instrumental causes of steatohepatitis. Purpose To investigate the protective effect of ethanolic extract of C. quadrangularis (EECQ) on the steatohepatitis associated with type 2 diabetes (DM) through inhibition of NOX4. Methods An experimental DM-induced steatohepatitis was developed by feeding a high-fat diet for 12 weeks in Sprague Dawley rats. Treatment of EECQ was given at a dose of 200 mg/kg (po), for six weeks. Glucose and insulin tolerance test was conducted. Hematoxylin and eosin and picrosirius red staining of liver sections was done. Steatosis and lobular inflammation were scored, and hepatocyte ballooning was assessed to confirm the NASH. qPCR, Immunofluorescence, and Immunoblotting determined the mRNA and protein expression of NOX4. Results NASH group rats manifested features of DM, marked by aggravated glucose and insulin tolerance tests. Moreover, the DM rats exhibited the presence of steatohepatitis, characterized by elevated serum lipid content, aminotransferases, and presence of steatosis, lobular inflammation, and ballooning in the liver section. Nevertheless, EECQ treatment prevented all of these abnormalities. Besides, the level of AGEs and the expression of its receptor, RAGE was found to be increased in DM rats. Parallelly, the expression of NOX4 and the accompanying level of ROS, oxidative stress markers, and inflammatory cytokines were determined to be surged in palmitic acid exposed HepG2 cells and DM rats. However, EECQ treatment exemplified safeguards from the soared level of the aforementioned markers. Conclusion Collectively, the above findings propounded the protective effect of EECQ against steatohepatitis. Nonetheless, further studies on humans necessitate to scrutinize and reinforce its therapeutic potential so that it may be employed as a remedy for DM-induced steatohepatitis.
Author: Lei He, Yuyong Chen, Zekai Ke, Mao Pang, Bu Yang, Feng Feng, Zizhao Wu, Chang Liu, Bin Liu, Xiaozuo Zheng, Tao Wu, Tao Shu
Publication: Genes
IF: 3.688
Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs)-derived exosomes (Exos) have anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic functions. miRNA-210 has also been confirmed to play a role in inhibiting proinflammatory cytokines. Herein, we aimed to explore the effects of Exos derived from miRNA-210-overexpressing BMSCs (BMSCs-210-Exos) and the mechanisms by which they provide protection to chondrocytes from lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced injury. BMSCs were transfected with or without miRNA-210. Exos substantially improved the proliferation of chondrocytes and inhibited LPS-induced cell apoptosis. Furthermore, BMSCs-210-Exos promoted the proliferation of chondrocytes and prevented LPS-induced cell apoptosis better than BMSCs-Exos not overexpressing miRNA-210. In addition, tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 21 (Tnfrsf21) expression was inhibited and the NF-κB pathway was attenuated by both BMSCs-Exos and BMSCs-210-Exos during LPS-induced chondrocyte injury. Collectively, these results suggest that BMSCs-210-Exos enhance the protection of chondrocytes from LPS-induced injury via the NF-κB pathway.
Author: Yang Yang, Jiajun Chen, Manli Tang, Chengla Yi, Wei Gao, Xiangjun Bai, Zhanfei Li & Fan Yang
Publication: Journal of Intensive Care
IF: 3.953
Despite improvements in antimicrobial therapy and supportive care, sepsis is still a major public health issue. Recently, CD100 and its receptor in the immune system CD72 were shown to play a major role in immune regulation. The purpose of this study was to investigate the expression and clinical correlations of CD72 and CD100 on circulating lymphocytes of septic patients.
Author: Meng Wang, Hua Xiong, Li Lu, Tongjian Zhu and Hong Jiang
Publication: Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity
IF: 7.31
Objectives. The gut microbiota and its metabolites are linked to inflammation and contribute to the progression of atrial fibrillation (AF), but the predictive value of the gut microbiota-derived metabolite lipopolysaccharide (LPS) for AF recurrence (RAF) is unknown. This study is aimed at investigating (1) the correlation between LPS and RAF and (2) its relationship with inflammation and atrial fibrosis. Method. We performed a single-centre retrospective analysis in 159 AF patients. Fasting plasma samples were collected, and an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay was used to determine the levels of serum LPS, interleukin-6 (IL-6), collagen type-1 C-terminal telopeptide (CITP), and transforming growth factor-β1 (TGFβ1). The cumulative risk for RAF was evaluated with Kaplan–Meier analysis. Cox proportional hazard analysis was carried out to predict the hazard of RAF. The correlations among LPS and IL-6, CITP, TGFβ1, and left atrial diameter (LAD) were analysed by Pearson’s correlation coefficient. Subsequent univariate and multivariable linear regression analyses were carried out to evaluate the connection between clinical variables and Log-LPS. Results. All 159 AF patients were included in this study. The proportion of persistent atrial fibrillation was 40.3%, the mean age was years, the proportion of males was 61.6%, and the mean LPS was pg/mL. After all patients were divided into tertiles according to the circulating LPS level, a total of 44 RAF occurred: 10 in the first tertile, 15 in the second tertile, and 19 in the third tertile (log-rank test ). Heart failure (hazard ratio 2.029, ), LAD (hazard ratio 1.064, ), Log-LPS (hazard ratio 5.686, ), and CITP (hazard ratio 6.841, ) independently predicted the risk of RAF. In all patients, univariate analysis showed that heart failure, LAD, hs-CRP, IL-6, CITP, and TGF-β1 were connected with Log-LPS. Multivariate linear regression analysis indicated that IL-6 and hs-CRP were independently and positively connected with Log-LPS. Conclusions. Our results indicated that circulating LPS was a predictor of RAF and may contribute to RAF incidence after ablation by increasing systemic inflammation and atrial fibrosis.
Author: Yihong Chen, Shan Zheng, Xiumei Zhao, Yi Zhang, Suchai Yu, Juanbing Wei
Publication: bioRxiv
IF: -
Endometritis seriously affects women’s normal life and work. It has been found that microRNA-123-3p (miR-124-3p) expression is abnormally high expression in the patients of chronic endometritis. However, the underlying mechanism for miR-124-3p regulation of endometritis development remains unclear. In our study, we treated human endometrial epithelial cells (HEECs) with LPS to simulate endometrial injury in vitro. Then, HEEC was treated with miR-124-3p mimics and miR-124-3p inhibitor. Next, exosomes were separated from bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs). In addition, BMSCs were co-cultured with HEEC. Later on, dual-luciferase reporter assay was carried out to validate the regulation between miR-124-3p and DUSP6. Results indicated that LPS inhibited the viability of HEEC in time and dose dependent manner. MiR-124-3p inhibitor reversed apoptosis and viability inhibition of HEEC which were induced by LPS. In addition, we also found exosomes could transfer miR-124-3p from BMSCs to HEEC. Besides, BMSCs/anti-miR-124-3p Exo was observed to abolish LPS-induced viability and proliferation inhibition of HEEC by inducing the apoptosis of HEEC. Moreover, BMSCs/anti-miR-124-3p Exo alleviated inflammation of HEEC induced by LPS via upregulating DUSP6 and downregulating p-p65 and p-ERK. Furthermore, BMSCs/anti-miR-124-3p Exo protected against LPS-induced endometritis in vivo by upregulating DUSP6 and downregulating p-p65 and p-ERK. In conclusion, we found that BMSCs/anti-miR-124-3p Exo might be a promising new alternative to treat endometritis.
Author: Serap Ozer Yaman, Fulya Balaban Yucesan, Cihan Orem, Birgul Vanizor Kural and Asim Orem
Publication: Journal of Clinical Medicine
IF: 4.964
Background: Postprandial lipemia (PPL) causes endothelial dysfunction by causing endothelial damage to lipoproteins that remain rich in triglycerides. Endocan is a proteoglycan with increased tissue expression, endothelial activation, and neovascularization. The aim of the study was to examine circulating endocan levels in PPL subjects by considering the degree of PPL response according to a high-fat test meal. The other aim was to determine the association between endocan levels and endothelial and inflammatory factors. Method: Fifty-four hyperlipidemic subjects and 28 normolipidemic subjects consumed the high-fat meal. Endocan, sICAM-1, sVCAM-1, and VEGFA as endothelial factors and IL-6 and LFA-1α as inflammatory factors were evaluated. Results: Fasting serum endocan, VEGFA, sICAM-1, sVCAM-1 IL-6, and LFA-1α levels were increased in the PPL group compared to the control group. The PPL group was divided into tertiles based on mean AUC levels. Endocan levels in tertile 3 were at the highest and were increased significantly compared to tertiles 1 and 2. AUC and endocan levels were positively correlated with other endothelial and inflammation factors. ROC analysis showed endocan levels to be one of the highest values. Conclusions: Circulating endocan is seen at significantly higher levels and independently associated with endothelial and inflammatory factors in postprandial lipemia and dyslipidemia.

 SingaporeSG
SingaporeSG ChinaCN
ChinaCN MalaysiaMY
MalaysiaMY IndonesiaID
IndonesiaID MyanmarMM
MyanmarMM


